Articles in the Guardian and my comment: "Ice found on moon surface, raising prospect of lunar colony" and "The Two_child policy in china"
My comment ; I met a woman in Paris a couple of years ago . She said she was a woman priest from a very rich christian community. She told me that "they" were planning to create space sky stations where people could live and florish and that was why it was Ok for people to have as many children as they wanted because the future of humanity was in Space. Meanwhile the earth could be used as a resource for this settelment in space project.
I was sure that she must have been joking but she was very convinced and as if in the know .... later on i read that China was scraping its limits on having children.
Birth controle will probably never happen in a rational way , some one like Indira Ghandi paid for her life for trying to sterilize people . Some countries try to have more children in order to conserve their language and cultural heritage .
Patches of frost around moon’s north and south poles could provide a source of water for humans, say astronomers
I was sure that she must have been joking but she was very convinced and as if in the know .... later on i read that China was scraping its limits on having children.
Birth controle will probably never happen in a rational way , some one like Indira Ghandi paid for her life for trying to sterilize people . Some countries try to have more children in order to conserve their language and cultural heritage .
Patches of frost around moon’s north and south poles could provide a source of water for humans, say astronomers

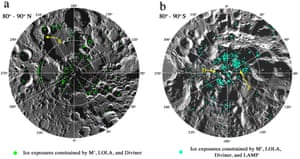
The scientists spotted the telltale signature of frozen water in infrared measurements taken by Nasa’s moon mineralogy mapper, an instrument that flew on India’s Chandrayaan-1 mission to the moon a decade ago.
The freshly-analysed data show that water ice lurks on the ground in a number of spots near the moon’s polar regions that are permanently in shade and so sheltered from the heat of the sun’s rays.
Most of the ice was found near the moon’s south pole around a cluster of craters named after scientists and explorers, including Haworth, Shoemaker, Sverdrup and Shackleton. In the north, the patches of ice appeared to be more isolated, according to Shuai Li at the Hawaii Institute of Geophysics and Planetology in Honolulu.
Follow-up measurements of the ice patches found that they tended to form where the surface temperature never crept above -163C, but temperature alone was not enough to guarantee frozen water: only 3.5% of the shadowy areas the scientists checked for water revealed notable signs of ice.
The Indian Space Agency launched its Chandrayaan-1 mission to the moon in 2008 and was swiftly rewarded with evidence of frozen water on the lunar surface a year later. Rather than sheets of ice on the surface, the water is thought to exist as water molecules bound to grains of moon dust.
Soon after the Indian feat, Nasa crashed a spacecraft into the 100km-wide Cabeus crater which is in permanent shade on the moon’s south pole. The intentional act of lunar violence threw up a plume of debris from which scientists were able to confirm the presence of water on the moon.
China could scrap two-child policy, ending nearly 40 years of limits
Draft of civil code being discussed this week contains no references to ‘family planning’

Chinese couples are limited to two children at present, after rules were relaxed from the infamous one-child policy that was in force from 1979 to 2016. Now officials are poised to enact a wide-ranging civil code that would end a policy that has been enforced through fines but was also notorious for cases of forced abortions and sterilisation in the world’s most populous country.
The Procuratorate Daily, a newspaper affiliated with the country’s prosecutor’s office, said the draft code omitted any reference to “family planning” – the current policy which limits couples to having no more than two children. The report did not indicate whether the new policy would raise the limit or allow an unlimited number of children.
The draft civil code, which is being discussed by the standing committee of the National People’s Congress this week, is set to be completed by 2020.
The draft code also includes “clear rules” to tackle the “intense problem of sexual harassment” reflected throughout society, state-run news agency Xinhua said on Tuesday, in an apparent nod to China’s growing #Metoo movement. Victims can demand perpetrators “assume civil liability” for committing sexual harassment through words or actions, or exploiting someone’s subordinate relationship, Xinhua reported.
The Communist party began enforcing a one-child policy in 1979 to slow population growth. The limit was raised to two children in 2016 as the nation scrambled to rejuvenate its ageing population of 1.4 billion.
Mary Gallagher, a politics professor at the University of Michigan, said: “[The government] now faces a colossal demographic cliff, as the working population shrinks and the ageing population rapidly expands. It also lacks a social insurance program that can adequately support its ageing population.”
Another concern is Chinese officials could “intervene as aggressively in pro-natalist policies as it did in anti-natalist policies,” she added. “This could have very negative effects on the position of women in the labor market, in society, and in the family.”
Childbirths have not increased as much as forecast since the two-child policy came into force, and there has been rising speculation the government will further ease restrictions.
The meetings of the standing committee of the National People’s Congress, a powerful body of lawmakers headed by Li Zhanshu, run until Friday.
Other proposed changes include a one-month cooling-off period before a divorce, during which either party can withdraw their application.
News of the proposed changes lit up social media. “So they want us to have more babies and less divorces?” wrote one user on Weibo, China’s equivalent of Twitter.

Speculation about a change grew this month after a government-issued postage stamp for the Year of the Pig in 2019 showed a porcine family complete with three piglets.
Couples have been in no rush to start larger families since the policy was loosened, with 17.9 million babies born in 2016 – just 1.3 million more than in the previous year, and half of what was expected, according to the National Bureau of Statistics.
Births in 2017 even slipped to 17.2 million, well below the official forecast of more than 20 million.
Hong Fincher said it remained to be seen how the Chinese government would implement any changes. She said incentives to have more children had not worked and the government might resort to other measures such as pressuring young women to get married and restricting abortions.
“Whatever policy they implement,” she said, “they will continue to control women’s reproductive rights.”
Agence France-Presse contributed to this report
Comments
Post a Comment